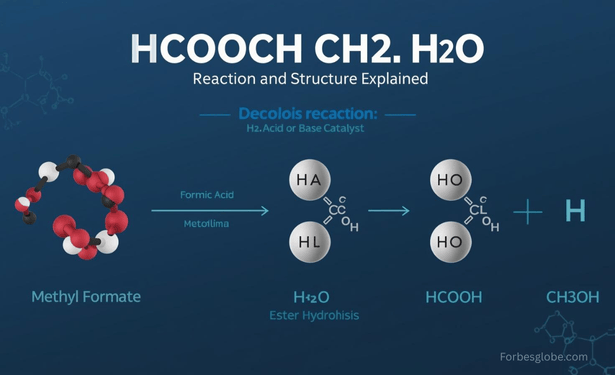
Many chemistry learners stumble when they see hcooch ch2 h2o. It looks like a formula, yet it doesn’t fit any standard molecule. In reality, this shorthand usually refers to the reaction between methyl formate (HCOOCH₃) and water (H₂O).
Understanding this helps decode a reaction that links organic chemistry concepts like ester hydrolysis, molecular structure, and product formation.
This article walks you through the reaction, structure, mechanism, and applications in clear and simple language, something competitors often overlook or overcomplicate.
What Does hcooch ch2 h2o Represent?
The expression hcooch ch2 h2o combines fragments that point to the interaction of methyl formate with water. Instead of being one compound, it represents a chemical process.
Breaking the formula down:
- HCOOCH₃ (methyl formate): An ester made from formic acid and methanol.
- H₂O (water): Reactant that triggers the breakdown of the ester.
Together they describe a hydrolysis reaction where the ester bond splits, producing formic acid and methanol.
Chemical identity explained:
- Name: Methyl formate (formic acid methyl ester)
- Formula: HCOOCH₃
- Family: Simple aliphatic ester
- Role: Demonstrates classic ester reactivity and hydrolysis behavior
This clarification eliminates a major online misconception, hcooch ch2 h2o isn’t a molecule, it’s a reaction expression.
Structural Overview and Molecular Geometry
Methyl formate has the molecular formula HCOOCH₃ and is the simplest formic acid ester.
Structure overview:
- Bond type: One carbonyl (C=O) and one alkoxy (O–CH₃) group
- Shape: Trigonal planar around the carbonyl carbon
- Polarity: The molecule is polar due to its asymmetric oxygen groups
- Reactivity: The carbonyl carbon is electrophilic, making it susceptible to attack by water molecules
This structure explains why methyl formate easily undergoes hydrolysis, the oxygen atoms pull electrons, creating a reactive center.
The hcooch ch2 h2o Reaction with Water
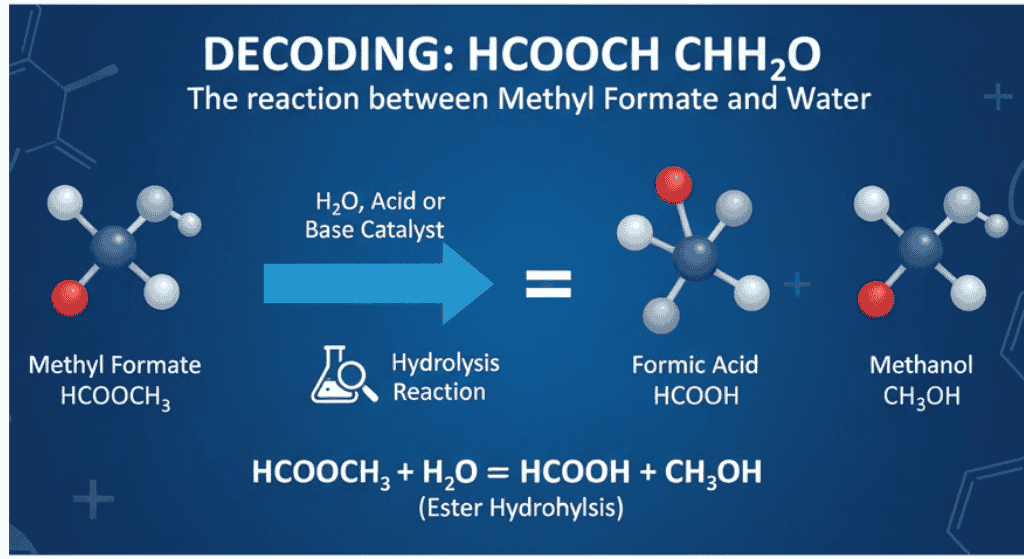
When methyl formate reacts with water, the process is called ester hydrolysis.
Reaction equation:
HCOOCH₃ + H₂O → HCOOH + CH₃OH
Here:
- HCOOH = Formic acid
- CH₃OH = Methanol
This reaction can occur under both acidic and basic conditions, though acid catalysis is more common in organic synthesis.
Reaction type:
| Reaction Condition | Description | Result |
| Acid-catalyzed hydrolysis | Protonation makes carbon more reactive | Yields formic acid & methanol |
| Base-catalyzed hydrolysis | Hydroxide ion attacks carbonyl directly | Rapid and nearly irreversible reaction |
Step-by-Step Reaction Mechanism
Breaking it down makes it easier to understand how the transformation happens.
Acid-catalyzed pathway:
- Protonation: Acid adds a proton to the carbonyl oxygen, making the carbon more electrophilic.
- Nucleophilic attack: Water attacks the carbonyl carbon.
- Intermediate formation: A temporary tetrahedral structure forms.
- Product release: Methanol leaves, and formic acid forms after deprotonation.
Base-catalyzed pathway:
- Nucleophilic attack: Hydroxide ion attacks the carbonyl carbon.
- Intermediate collapse: Methoxide ion departs.
- Product formation: The remaining ion forms formate, which becomes formic acid.
These steps demonstrate how acid and base catalysis differ while reaching the same end products.itution.
Read more: Why Disohozid Are Bad for Your Health: What You Need to Know
Kinetics and Activation Energy
The rate of hydrolysis depends on concentration, temperature, and catalyst type.
- Acidic conditions: Usually first order in ester; rate increases with acid strength.
- Basic conditions: Often second order, first order in both ester and hydroxide ion.
- Activation energy: Approximately 55–65 kJ/mol under moderate conditions.
- Practical insight: Reaction rates can be measured using GC-MS or HPLC by tracking methanol formation.
Understanding kinetics helps chemists adjust conditions for industrial-scale reactions while minimizing unwanted side reactions.
Reaction Conditions
Reactions behave differently depending on lab or industrial settings.
Here’s a quick guide:
| Factor | Optimal Range | Importance |
| Catalyst type | HCl or NaOH | Controls speed and yield |
| Temperature | 60–80°C (acidic) | Speeds up reaction |
| Solvent | Aqueous medium | Ensures good reactant contact |
| pH control | 2–4 (acidic) or >10 (basic) | Determines direction of equilibrium |
Lab checklist:
- Stir continuously for uniform reaction
- Add catalyst slowly
- Keep away from open flame (flammable vapors)
- Neutralize the reaction before disposal
Industrial and Laboratory Importance
Hydrolysis of methyl formate is not just academic, it has practical relevance.
Industrial uses
- Precursor for formic acid production
- Solvent in coating and extraction processes
- Intermediate in fragrance and flavor manufacturing
Laboratory applications
- Demonstrating ester reactivity in organic chemistry courses
- Studying reaction kinetics and catalysis
- Preparing samples for analytical testing (e.g., GC-MS)
The reaction’s simplicity makes it a reliable example for both learning and applied research.
Safety, Hazards, and Handling Guidelines
Safety information is often overlooked, yet it’s crucial when dealing with esters and alcohols.
Precautions
- Always work in a fume hood
- Wear gloves, goggles, and a lab coat
- Avoid inhalation or direct contact with vapors
- Methanol toxicity: Even small amounts can cause harm
Storage
- Store in cool, ventilated areas
- Keep away from heat sources and oxidizers
- Label containers properly and check SDS sheets before handling
Understanding safety isn’t just about compliance, it protects researchers and maintains lab integrity.
Environmental and Sustainability Aspects
From a sustainability viewpoint, methyl formate holds promise as a green solvent alternative.
Eco-related points
- It biodegrades faster than many industrial solvents.
- When sourced from renewable methanol, it can support low-carbon manufacturing.
- Process optimization, lower temperatures and better catalysts, reduces energy demand and waste.
This makes the reaction relevant to discussions on green chemistry and sustainable process design.
Common Misconceptions About hcooch ch2 h2o
Many online articles misrepresent hcooch ch2 h2o. Let’s set the record straight.
| Misconception | Correction |
| It’s a real molecule. | It’s a shorthand for methyl formate reacting with water. |
| CH₂ is a separate species. | CH₂ here represents part of the structure, not an isolated atom. |
| Reaction can be done at home. | Absolutely not. Proper lab control and ventilation are mandatory. |
| Hydrolysis is always fast. | Rate depends on conditions—acid/base strength and temperature matter. |
Being precise with these points improves accuracy and builds scientific credibility.
Read more: MT6761 CascabelK Unlock Software: Unlock Your Device Easily
Frequently Asked Questions
What does hcooch ch2 h2o mean?
It’s shorthand for the reaction between methyl formate and water producing formic acid and methanol.
Is methyl formate naturally occurring?
It occurs in trace amounts in the atmosphere and some plant emissions.
What type of reaction is this?
An ester hydrolysis, which can be catalyzed by acid or base.
What are the practical uses of this reaction?
Producing formic acid, studying reaction kinetics, and developing sustainable solvents.
How should it be handled safely?
Use proper protective gear, ensure ventilation, and follow SDS instructions.
Summary and Call to Action
Understanding hcooch ch2 h2o clarifies more than a confusing formula, it teaches the logic behind ester reactions, molecular structure, and hydrolysis mechanisms that define organic chemistry.
In summary:
- It stands for methyl formate reacting with water.
- The reaction produces formic acid and methanol.
- It demonstrates key concepts in structure, polarity, and catalysis.
- Its study supports safe, sustainable, and smart chemical design.
Call to Action:
If you found this guide helpful, explore more about organic reaction mechanisms or bookmark this post for quick reference. Stay curious, stay safe, and keep exploring the fascinating world of chemistry!